THE WHY
/
How And Why You Should Take Clean Vitamins
We may choose ‘natural’ vitamins as they sound more wholesome, perhaps more effective, more, well, natural. But is this the case?
Consistency and Standardisation
To meet regulatory health standards and have predictable outcomes for consumers, synthetic vitamins can be produced to an exact specification and provide a consistent amount of each nutrient in each pill.
Cost
It can be labour-intensive and expensive to harvest nutrients naturally. Large scale manufacturing of synthetic vitamins is often a lot lower cost (this drives the cost down for you as well).
Bio-availability
In layman’s terms, bioavailability is the natural ease for your body to absorb a nutrient. Some synthetic vitamins are developed to increase absorption and will actually be better for you than a natural alternative.
Synthetic vitamins are more stable and have a longer shelf life than natural ones; this means they remain effective for a longer time.
It’s also worth noting that if most vitamins had all natural ingredients they would be around the size of a golf ball.

Blood Tests
A blood test can pinpoint specific nutrient deficiencies.
Some vitamins and minerals can be harmful in excessive amounts.
Harmful may be a little dramatic for this fact but as an example; if you have excessive amounts of Vitamin C- this can impact the way your body absorbs Vitamin B12.
Vitamins and minerals can interfere with medicines aKa vitamin K can affect blood thinners so it is always best to get this checked.
If you don’t get a blood test, you can look at what people are typically deficient in- to give you an idea of what it is you’re more likely to be in need of.
Visit the NHS for more information about Blood Tests.

Nutrients To Look Out For
Here are the most common nutrient deficiencies in the UK for women age 18+ and what foods should be in your diet to help maintain a healthy amount.
IRON: seeds, nuts, dried fruits, pulses
CALCIUM: dairy products, nuts (like almonds), tahini, spinach, broccoli, figs, calcium-set tofu, calcium-fortified plant milk
VITAMIN K: helps calcium be absorbed by your teeth and bones, it is no use having a suitable amount of one without the other. Luckily, Vitamin K is found in lots of green things- spinach, broccoli, kiwi, spinach, kale, cabbage
VITAMIN D: fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel), mushrooms, fortified breakfast foods, egg yolks
VITAMIN B12: if you are eating a plant based diet, this vitamin most likely needs to be replaced with a supplement as it is most commonly found in animal foods; red meats, shellfish
We can’t tell you the exact vitamins and minerals that would be perfect for you but we have sourced some amazing brands doing wonderful things in the vitamin world.

Wild Nutrition
Wild Nutrition select fresh, organic foods like citrus, carrots, nutrient-rich yeast, lactobacillus, or split yellow peas. They prioritize sourcing ingredients directly from their country of origin for true traceability.
To start the process; they reduce the food to a fine paste using organic, non-GMO ingredients- using every part of the food, including seeds and skin, ensuring no waste.
Putting the Nutrients In
- Add a single, essential nutrient (e.g., Magnesium, Iron, Vitamin C) to the food paste.
- Stir in a glycoprotein mixture to help integrate the nutrient into the paste.
The Science Bit
- The glycoprotein mixture carries the nutrient into the food paste matrix.
- Combine the nutrient and whole food to create a comprehensive supplement.
The Magic of Food-Grown
- The nutrient bonds, grows, and transforms within the food paste.
- Result: A potent, nutrient-dense food complex that the body can easily recognize and absorb.
The Finished Supplement
- Gently dry the food paste with filtered air in a low-heat environment to preserve nutrient stability.
- Encapsulate in vegetable-derived cellulose capsules, free from binding agents and fillers.
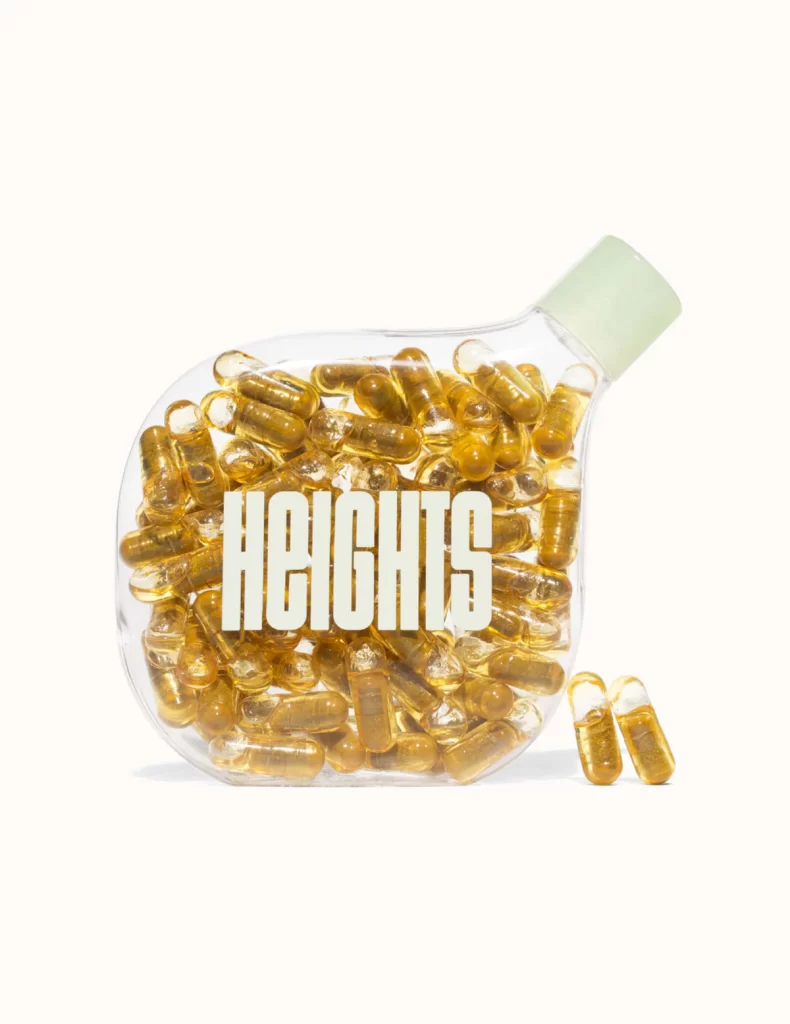
Heights
Heights are made in small batches; this ensures freshess and high quality when it gets to you. Small-batch manufacturing also means that when exciting new scientific research comes out, they can adjust the formula to make it better.
Brain first. This means every decision considers the effect it will have on the brain first.
That starts with getting into the data. If something’s in Heights, it’s in there because there’s a body of research to back it up. They review their formula every 3 months to keep up with emerging scientific evidence around nutrition for the brain.
Do no harm. Many supplements contain harmful caking agents like talcum powder. They also can contain heavy metals, chemicals, and other nasty and harmful contaminants not listed on the label. Gross.
Heights are manufactured in Europe (the safety regulations are stricter there).
Unlike most other supplements, Heights wrap their nutrients in omega 3 (from algae oil) to make sure every vitamin is absorbed. Omega 3 is not only amazing for you and your brain, using it in this way also means that the other nutrients are protected from your stomach acid, so they can reach your intestine where they’re absorbed into the bloodstream.
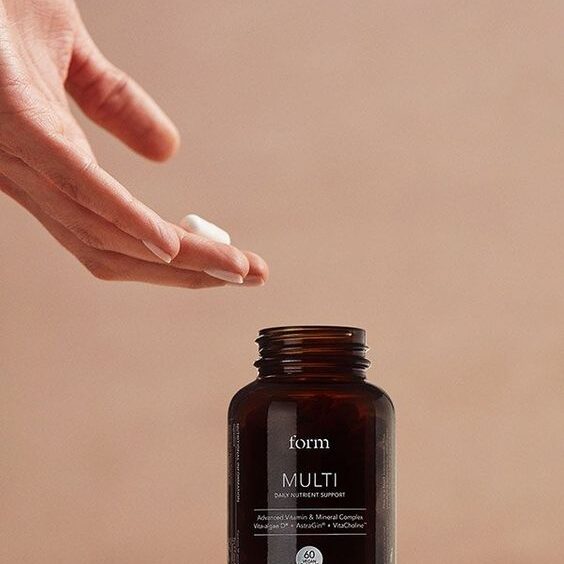
Form Nutrition
Form Nutrition believe you can become the best version of yourself while being considerate of others.
This philosophy guides everything they do.
They’ve created plant-based proteins for your body and responsibly-sourced nootropics for your mind. Their products are scientifically backed and designed to enhance your performance.
They believe in business as a force for good, ensuring their impact is beneficial for you and the community.
✔️Vegan
✔️Dairy Free
✔️Gluten Free
✔️GMO and Soy Free
✔️Glass Jar
With every product you purchase from Form, you help support those in need via the Form Feeding Fund at Bansang Hospital in The Gambia.
We Would Love To Hear From You
Are you a nutritionist and could add to our article?
Contact: clare@thewellnest.club